Dr. Amrita Khatri
M.D., B.H.M.S.Book Appointment
Fungal infection
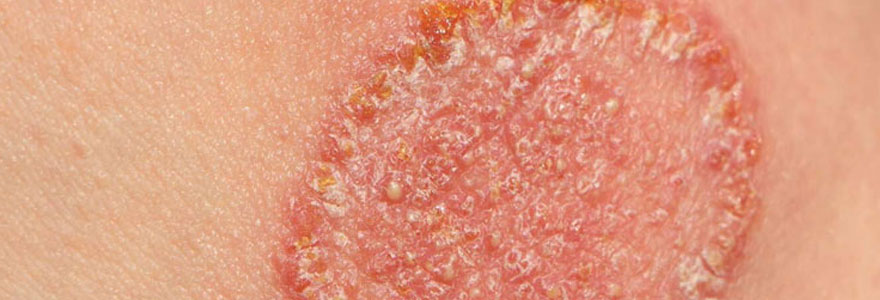
Fungal infections, also known as mycoses, can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, nails, mouth, throat, genitals, and internal organs. Fungal infections are caused by various types of fungi and can range from mild and easily treatable conditions to severe and potentially life-threatening diseases.
Symptoms of Fungal Infection
- Itching: Persistent itching in the affected area, which can be intense.
- Redness: Red or inflamed patches of skin, often with a rash-like appearance.
- Scaling or Flaking Skin: Skin that becomes dry, flaky, or scaly, particularly in areas like the feet (athlete's foot) or scalp (dandruff).
- Cracked or Peeling Skin: Cracks or peeling skin, especially between the toes or fingers.
- Blisters: Small fluid-filled blisters that may burst and crust over.
- Discoloration: Changes in skin color, with areas appearing darker or lighter than the surrounding skin.
- Odor: Foul or unpleasant odor, particularly in areas like the feet or groin.
- Thickened or Discolored Nails: In cases of nail fungus, the nails may become thickened, brittle, or yellowish-brown in color.
- Rash: A rash that may spread over time and become more severe.
Causes of Fungal Infection
- Moisture and Warmth: Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making areas like the feet, groin, and underarms more susceptible.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate hygiene practices, such as not drying the skin thoroughly after bathing, can promote fungal growth.
- Weakened Immune System: A weakened immune system, due to conditions like diabetes, HIV, or use of immunosuppressive medications, increases the risk of fungal infections.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating, especially in hot and humid climates, can create the ideal conditions for fungal growth.
- Tight or Non-Breathable Clothing: Wearing tight or synthetic clothing that doesn't allow the skin to breathe can trap moisture and heat, promoting fungal infections.
- Close Contact: Direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces, such as communal showers or locker rooms, can spread fungal infections.
- Use of Antibiotics: Long-term or frequent use of antibiotics can disrupt the balance of normal skin flora, allowing fungi to proliferate.
- Obesity: Increased skin folds and areas where skin rubs against skin can create moist environments prone to fungal infections.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can lead to a higher risk of infections, including fungal infections.


