Dr. Amrita Khatri
M.D., B.H.M.S.Book Appointment
Urticaria
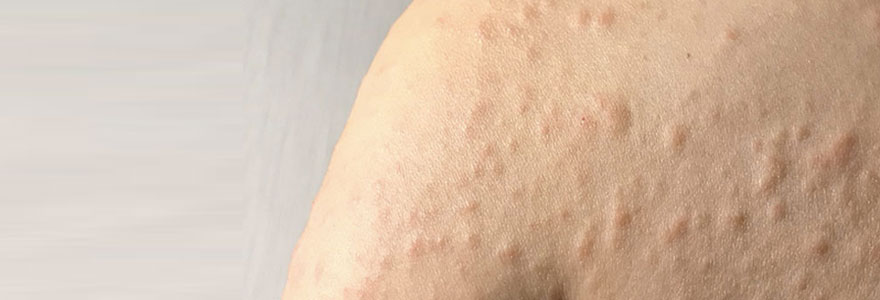
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of itchy, raised, and red or pale welts or bumps on the skin. These welts can vary in size and shape and often appear and disappear within hours. Urticaria can be acute (lasting for a few hours to several weeks) or chronic (persisting for more than six weeks).
Symptoms of Urticaria
- Itchy Rash: Raised, itchy welts or hives on the skin that can vary in size and shape.
- Red or Pink Welts: Red or pink patches on the skin that may be surrounded by a pale halo.
- Swelling: Swelling in areas such as the face, lips, throat, or limbs, often accompanied by itching.
- Blisters: Some hives may appear as small, fluid-filled blisters.
- Transitory: Hives often come and go, and may move to different areas of the body over time.
- Variable Size: Welts can range from small spots to large areas, sometimes merging to form bigger patches.
Causes of Urticaria
- Allergic Reactions: Common allergens include certain foods (e.g., nuts, shellfish), medications, or insect stings.
- Infections: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections can trigger hives.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to environmental triggers such as pollen, pet dander, or extreme temperatures can cause hives.
- Stress: Emotional stress or anxiety can sometimes contribute to the development of hives.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or aspirin, may cause hives as a side effect.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions where the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues, such as lupus or thyroid disease, can be associated with chronic urticaria.
- Physical Triggers: Physical stimuli such as pressure, sunlight, or exercise can induce hives in some individuals.
- Food Additives: Certain food additives, preservatives, or colorants may trigger allergic reactions leading to hives.
- Chronic Urticaria: In some cases, the exact cause of chronic urticaria may be unknown, but it can persist for months or years.


