Dr. Amrita Khatri
M.D., B.H.M.S.Book Appointment
Warts
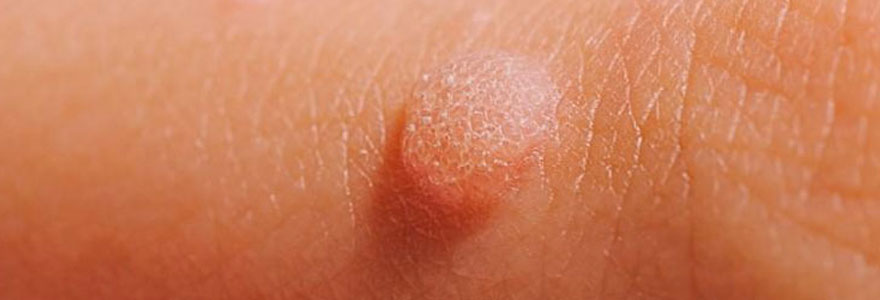
Warts are benign (non-cancerous) skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear on various parts of the body, including the hands, feet, face, and genital area. Warts are common and can affect people of all ages, although they are more prevalent in children and adolescents.
Symptoms of Warts
- Small Growths: Small, raised bumps on the skin, which can vary in size and shape.
- Rough Surface: Warts often have a rough, grainy surface that may feel hard to the touch.
- Flat or Raised: Warts can appear flat or raised, and their surface may have tiny black dots (which are small blood vessels).
- Localized Discomfort: Some warts may cause minor discomfort, itching, or tenderness, especially if located on pressure points such as the soles of the feet.
- Varying Colors: They may be flesh-colored, white, pink, or tan.
Causes of Warts
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Warts are caused by an infection with HPV, which is transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces.
- Skin-to-Skin Contact: Direct contact with warts on another person's skin can spread the virus.
- Infected Surfaces: Walking barefoot on contaminated surfaces, such as public showers or swimming pool areas, can lead to plantar warts.
- Immune System Factors: People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to developing warts.
- Minor Skin Injuries: Cuts, scratches, or other minor injuries to the skin can provide an entry point for the virus.
- Autoinoculation: Warts can spread from one part of the body to another, often through touching or scratching the warts and then touching other areas.


